Effective classroom management is key to creating a productive and engaging learning environment. Different teachers have different styles when it comes to managing student behavior. In this blog, we will explore the four main categories of classroom management styles and help you identify your preferred approach.
| Features | Authoritarian Management | Authoritative Management | Permissive Management | Indulgent Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rules and Expectations | Emphasizes strict rules and regulations | Sets clear expectations with warmth and firmness | Provides minimal rules and structure | Fosters flexibility with minimal rules |
| Hierarchical Structure | Maintains a top-down authority structure | Balances authority with student autonomy | Promotes student autonomy and independence | Nurtures positive relationships with students |
| Instruction | Utilizes direct instruction and firm guidance | Offers guidance with flexibility and empathy | Allows for student-driven learning experiences | Encourages creativity and self-expression |
| Discipline | Applies strict discipline with swift consequences | Implements constructive discipline techniques | Relies on positive reinforcement | Emphasizes emotional support and understanding |
| Student Autonomy | Limits student autonomy and decision-making | Encourages student participation and input | Prioritizes student choice and independence | Empowers students with autonomy and freedom |
| Teaching Styles | Authoritarian Management | Authoritative Management | Permissive Management | Indulgent Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directive | Teacher-centered approach with rigid instruction | Balances teacher guidance with student input | Student-centered approach with minimal guidance | With limited collaboration, teacher holds primary control |
| Authoritative | Asserts authority with clear directives | Establishes authority with warmth and respect | Facilitates learning with minimal intervention | Builds positive relationships through empathy |
| Collaborative | With limited collaboration, the teacher holds primary control | Encourages collaboration and mutual respect | Fosters peer interaction and group activities | Promotes collaboration and shared decision-making |
| Drawbacks | Authoritarian Management | Authoritative Management | Permissive Management | Indulgent Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Limits student autonomy and creativity | Potential inconsistency in enforcement | Potential lack of structure and discipline | Potential for lack of accountability |
| Engagement | May inhibit student engagement and participation | Requires strong teacher-student rapport | A balanced approach may require more time investment | This may lead to disengagement or apathy |
| Resentment | Students may resent strict rules and authority | Risk of confusion with mixed messages | Lack of clear boundaries may lead to confusion | This may result in a lack of respect for authority |
| Learning Opportunities | Focus on discipline may detract from instructional time | Balanced approach may require more time investment | Lack of structure may lead to missed learning opportunities | Emphasis on emotional support may detract from academic focus |
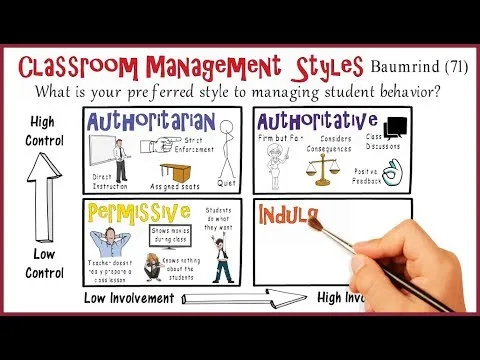
Authoritarian Classroom Management
The first category is authoritarian management, where teachers exhibit high control but low involvement with students. In this style, the teacher is very controlling and might rely on lecture-driven lessons, often reading off a PowerPoint or simply talking about the content. Students are expected to sit quietly and not ask questions. Classroom rules are strictly enforced, and the teacher is firm and inflexible. Assigning seats for the entire year is a common practice among authoritarian teachers, as they prefer an organized classroom with students in one place.
Authoritarian management represents a distinct approach to classroom management characterized by strict discipline, hierarchical structure, and clear rules and expectations. While this approach may be effective in maintaining order and control within the classroom, it also raises concerns about limited student autonomy and potential negative effects on student motivation and engagement. By understanding the key features and principles of authoritarian management and implementing strategies to effectively utilize its techniques, educators can create a structured and disciplined learning environment that supports student achievement and fosters a positive classroom climate. However, it is essential to recognize that authoritarian management may not be suitable for every classroom or teaching style and should be implemented with careful consideration of its potential impact on students’ social, emotional, and academic development. Ultimately, the goal of classroom management is to create a supportive and engaging learning environment where all students can thrive academically and socially, and educators must continuously strive to refine their practices to meet the diverse needs of their students.
In classroom management, there exists a spectrum of approaches, each with its unique philosophies, methodologies, and outcomes. One such approach that has garnered attention and debate is authoritarian management. Rooted in a top-down hierarchy of authority, authoritarian management places a strong emphasis on discipline, control, and obedience within the classroom setting. While often criticized for its perceived rigidity and lack of student autonomy, proponents argue that authoritarian management can effectively maintain order and facilitate learning in certain contexts.
At its core, authoritarian management is characterized by the centralization of authority in the hands of the teacher, who assumes the role of an authoritative figure responsible for establishing and enforcing rules and expectations. In an authoritarian classroom, students are expected to comply with directives without question, with consequences for non-compliance typically swift and decisive. This approach is rooted in the belief that a structured and disciplined environment is essential for fostering academic achievement and preparing students for success in the broader society.
Features of Authoritarian Classroom Management:
To understand authoritarian management more comprehensively, it is essential to explore the key features and principles that underpin this approach. While there may be variations in implementation, the following features are commonly associated with authoritarian management:
- Clear Rules and Expectations:
- Authoritarian classrooms are characterized by clearly defined rules and expectations, which are communicated explicitly to students.
- These rules govern various aspects of classroom behavior, including attendance, participation, respect for authority, and adherence to academic standards.
- Students are expected to comply with these rules at all times, with consequences for violations clearly outlined and consistently enforced.
- Hierarchical Structure:
- Authoritarian management maintains a hierarchical structure within the classroom, with the teacher occupying a position of authority at the top of the hierarchy.
- Students are positioned as subordinate to the teacher, expected to follow instructions and directives without question.
- This hierarchical structure reinforces the teacher’s role as the ultimate authority figure, responsible for maintaining order and discipline within the classroom.
- Direct Instruction:
- In an authoritarian classroom, instruction is typically delivered in a direct and structured manner, with the teacher assuming primary control over the flow of information.
- Teachers may employ traditional teaching methods such as lectures, drills, and rote memorization to convey content to students.
- Students are expected to listen attentively and follow along with the teacher’s instructions, with limited opportunities for independent exploration or inquiry-based learning.
- Strict Discipline:
- Discipline is a central tenet of authoritarian management, with an emphasis on swift and consistent enforcement of consequences for misbehavior.
- Teachers may employ punitive measures such as verbal reprimands, loss of privileges, detention, or referrals to the principal’s office to address infractions.
- The goal of strict discipline is to maintain order and control within the classroom, ensuring that learning can proceed without disruption.
- Limited Student Autonomy:
- Authoritarian management tends to restrict student autonomy, with limited opportunities for students to make decisions or express their opinions.
- Teachers retain primary control over classroom activities, assignments, and assessments, with students expected to comply with instructions and guidelines provided by the teacher.
- While students may have some degree of input in certain classroom activities, such as group projects or discussions, the overall structure and direction of learning are determined by the teacher.
How to Use Authoritarian Management in the Classroom
Implementing authoritarian management in the classroom requires careful planning, consistent implementation, and a nuanced understanding of its principles and potential drawbacks. While this approach may not be suitable for every classroom or teaching style, there are certain strategies that educators can employ to effectively utilize authoritarian management techniques:
- Establish Clear Rules and Expectations:
- Begin by establishing clear and concise rules and expectations for classroom behavior, academic performance, and interaction with peers.
- Communicate these rules to students at the beginning of the school year and reinforce them regularly through reminders and review sessions.
- Be explicit about the consequences of violating these rules, ensuring that students understand the potential outcomes of their actions.
- Maintain a Structured Environment:
- Create a structured learning environment that promotes order and discipline, with clearly defined routines and procedures for various classroom activities.
- Develop a consistent daily schedule that outlines the sequence of instructional activities, transitions, and breaks, allowing students to anticipate and prepare for upcoming tasks.
- Minimize disruptions and distractions within the classroom by enforcing expectations for attentive listening, respectful behavior, and active participation.
- Establish Teacher Authority:
- Assert your authority as the teacher by setting clear boundaries and expectations for student behavior and academic performance.
- Communicate confidence and authority in your interactions with students, speaking and acting with authority when delivering instructions or addressing disciplinary issues.
- Avoid wavering or being swayed by student resistance or attempts to challenge your authority, remaining firm and consistent in your responses.
- Enforce Consequences Consistently:
- Be consistent in enforcing consequences for misbehavior, ensuring that students understand the link between their actions and the resulting outcomes.
- Address infractions promptly and decisively, employing appropriate consequences that are commensurate with the severity of the behavior.
- Follow through on disciplinary measures consistently, avoiding leniency or favoritism in your responses to student behavior.
- Foster Respect and Cooperation:
- While maintaining authority and discipline, strive to foster a positive and respectful classroom climate characterized by mutual respect and cooperation.
- Encourage students to respect one another’s opinions and perspectives, even when they disagree with them, fostering a culture of open dialogue and constructive communication.
- Model respectful behavior and positive interactions in your interactions with students, demonstrating empathy, fairness, and professionalism at all times.
Authoritative Classroom Management
Moving down we have authoritative management, which combines high control with high involvement. The authoritative teacher enforces rules but also listens to students. They aim to give students their voice and encourage classroom discussions. The authoritative style is both firm and fair, with teachers caring deeply about their students’ success. Positive feedback is common, and teachers consider the circumstances when addressing inappropriate behavior. This style fosters a supportive learning environment.
there exists a spectrum of approaches, each with its unique philosophies, methodologies, and outcomes. One such approach that has garnered attention and debate is authoritative management. Rooted in a balance of firmness and warmth, authoritative management emphasizes setting clear expectations while also nurturing positive relationships with students. Unlike authoritarian management, which prioritizes strict control and obedience, authoritative management seeks to foster autonomy and responsibility in students while maintaining a structured and supportive learning environment.
Features:
To understand authoritative management more comprehensively, it is essential to delve into the key features and principles that underpin this approach. While there may be variations in implementation, the following features are commonly associated with authoritative management:
- Clear Expectations and Consistency:
- Authoritative classrooms are characterized by clear and consistent expectations for behavior, academic performance, and classroom participation.
- Teachers communicate these expectations explicitly to students and consistently enforce them, providing predictability and structure in the learning environment.
- By setting clear boundaries and guidelines, teachers establish a framework for students to understand what is expected of them and how they can succeed.
- Positive Teacher-Student Relationships:
- Central to authoritative management is the cultivation of positive and supportive relationships between teachers and students.
- Teachers strive to build rapport with students, demonstrating warmth, empathy, and respect in their interactions.
- By fostering a sense of trust and mutual respect, teachers create an environment where students feel valued and supported in their academic and personal growth.
- Responsiveness and Flexibility:
- Authoritative teachers are responsive to the individual needs and interests of students, adapting their teaching approaches and strategies accordingly.
- Teachers encourage student input and feedback, incorporating student perspectives into classroom decision-making and planning.
- By being flexible and responsive, teachers demonstrate their commitment to meeting the diverse needs of their students and promoting a sense of ownership in the learning process.
- High Expectations for Behavior and Achievement:
- While authoritative teachers maintain warm and supportive relationships with students, they also hold high expectations for behavior and academic achievement.
- Teachers believe in the potential of all students to succeed and provide the necessary support and encouragement to help them reach their full potential.
- By setting challenging yet attainable goals and providing constructive feedback, teachers motivate students to strive for excellence and take pride in their accomplishments.
- Constructive Discipline and Guidance:
- In authoritative classrooms, discipline is approached constructively and respectfully, focusing on teaching rather than punishment.
- Teachers use discipline as an opportunity to help students learn from their mistakes, develop self-regulation skills, and make positive choices.
- By providing guidance and support, teachers empower students to take responsibility for their actions and make positive contributions to the classroom community.
How to Use Authoritative Management in the Classroom:
Implementing authoritative management in the classroom requires a thoughtful and intentional approach that balances structure with flexibility, and authority with warmth. While this approach may not be suitable for every classroom or teaching style, there are certain strategies that educators can employ to effectively utilize authoritative management techniques:
- Establish Clear Expectations:
- Begin by establishing clear and consistent expectations for behavior, academic performance, and classroom participation.
- Communicate these expectations to students positively and constructively, emphasizing the importance of mutual respect and responsibility.
- Provide students with opportunities to contribute to the development of classroom norms and guidelines, promoting a sense of ownership and buy-in.
- Build Positive Relationships:
- Invest time and effort in building positive and supportive relationships with students, demonstrating warmth, empathy, and respect in your interactions.
- Get to know your students as individuals, showing genuine interest in their interests, strengths, and challenges.
- Be approachable and accessible to students, creating an environment where they feel comfortable seeking support and guidance.
- Foster Autonomy and Responsibility:
- Empower students to take ownership of their learning by providing opportunities for autonomy and independence.
- Encourage students to set goals, make decisions, and take initiative in their academic pursuits.
- Provide guidance and support as needed, but allow students the freedom to explore and discover solutions on their own.
- Maintain High Expectations:
- Hold high expectations for behavior and academic achievement, believing in the potential of all students to succeed.
- Communicate your belief in students’ abilities and provide the necessary support and resources to help them reach their goals.
- Celebrate students’ successes and accomplishments, reinforcing their confidence and motivation to excel.
- Use Positive Reinforcement:
- Recognize and reinforce positive behaviors and contributions in the classroom, using praise, encouragement, and rewards to motivate students.
- Acknowledge students’ efforts and progress, highlighting their strengths and areas of growth.
- Create a culture of positivity and appreciation, where students feel valued and supported in their academic and personal development.
Permissive Classroom Management
On the lower end of the control spectrum, we find permissive management, characterized by very little control and limited student involvement. Unfortunately, teachers with this style often lack passion for teaching and see it merely as a way to pay the bills. They may not take the time to prepare lesson plans or establish classroom rules and procedures. Consequently, permissive classrooms can be chaotic, with students doing as they please. Teachers may resort to showing movies during class time instead of actively teaching. The lack of care for students and teacher-student relationships is a significant drawback of this management style.
In the landscape of classroom management, educators often explore various approaches to fostering a conducive learning environment. One such approach that has garnered attention is permissive classroom management. Unlike authoritarian management, which emphasizes strict control and adherence to rules, permissive management adopts a more lenient and flexible stance, allowing students greater autonomy and independence in their learning journey. While some critics argue that permissive management may lead to chaos and lack of discipline, proponents assert that it cultivates a sense of responsibility and empowerment among students, fostering a positive and inclusive classroom culture.
Features:
To gain a comprehensive understanding of permissive classroom management, it’s essential to examine the key features and principles that guide this approach. While implementations may vary, the following features are commonly associated with permissive management:
- Flexibility and Autonomy:
- Permissive management prioritizes flexibility and autonomy, allowing students greater freedom to make choices and decisions regarding their learning.
- Teachers provide students with opportunities to explore topics of interest, select learning activities, and express their opinions and ideas.
- By fostering a sense of ownership and independence, permissive management empowers students to take responsibility for their learning and engage more deeply in the educational process.
- Minimal Rules and Structure:
- In contrast to authoritarian management, which emphasizes strict rules and regulations, permissive management adopts a more relaxed approach to classroom rules and structure.
- Teachers may establish basic guidelines for behavior and academic performance but allow for greater flexibility and discretion in their enforcement.
- The emphasis is on promoting a culture of trust and respect, where students feel empowered to make choices and contribute to the learning environment.
- Emphasis on Creativity and Self-Expression:
- Permissive classrooms prioritize creativity and self-expression, encouraging students to explore their interests, passions, and talents.
- Teachers provide opportunities for students to engage in open-ended and inquiry-based activities, allowing for diverse perspectives and solutions.
- By fostering a culture of creativity and self-expression, permissive management nurtures students’ confidence, curiosity, and innovation.
- Collaborative Learning and Peer Interaction:
- Permissive management promotes collaborative learning and peer interaction, recognizing the value of cooperation and teamwork in the learning process.
- Teachers facilitate group activities, discussions, and projects that encourage students to work together, share ideas, and learn from one another.
- By fostering a sense of community and collaboration, permissive management creates a supportive and inclusive learning environment where students feel valued and respected.
- Focus on Positive Reinforcement:
- In permissive classrooms, positive reinforcement is used to motivate and encourage students, rather than relying on punitive measures or strict discipline.
- Teachers acknowledge and celebrate students’ achievements, efforts, and contributions, reinforcing desired behaviors and attitudes.
- By emphasizing positivity and encouragement, permissive management cultivates a culture of affirmation and support, where students feel valued and motivated to excel.
How to Use Permissive Management in the Classroom:
Implementing permissive management in the classroom requires a thoughtful and intentional approach that balances freedom with responsibility and autonomy with structure. While this approach may not be suitable for every classroom or teaching style, there are certain strategies that educators can employ to effectively utilize permissive management techniques:
- Establish Clear Expectations:
- While permissive management emphasizes flexibility and autonomy, it is essential to establish clear expectations and guidelines for behavior and academic performance.
- Communicate these expectations to students positively and constructively, emphasizing the importance of mutual respect and responsibility.
- Provide students with opportunities to contribute to the development of classroom norms and guidelines, promoting a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Foster a Culture of Respect:
- Create a classroom environment where respect for oneself, peers, and the learning process is valued and celebrated.
- Model respectful behavior and positive communication in your interactions with students, demonstrating empathy, fairness, and understanding.
- Encourage students to express their opinions and ideas openly and respectfully, fostering a culture of mutual respect and acceptance.
- Provide Opportunities for Choice and Voice:
- Empower students to take ownership of their learning by providing opportunities for choice and voice in the classroom.
- Offer a variety of learning activities and assignments that cater to diverse interests, learning styles, and abilities.
- Encourage students to share their perspectives, ideas, and questions, promoting active engagement and participation in the learning process.
- Emphasize Collaboration and Peer Learning:
- Foster a collaborative learning environment where students work together, share ideas, and learn from one another.
- Facilitate group activities, discussions, and projects that encourage cooperation, teamwork, and peer interaction.
- Provide guidance and support as needed, but allow students the freedom to collaborate and problem-solve independently.
- Use Positive Reinforcement:
- Recognize and reinforce positive behaviors and contributions in the classroom, using praise, encouragement, and rewards to motivate students.
- Acknowledge students’ efforts and progress, highlighting their strengths and areas of growth.
- Create a culture of positivity and affirmation, where students feel valued and supported in their academic and personal development.
Indulgent Management
Lastly, we have indulgent management, which strikes a balance between little control and high involvement. Indulgent teachers are dedicated to their teaching careers and work hard to create fun and exciting lessons. They believe in a student-empowered learning model and allow students to have a say in classroom decisions. These teachers prioritize building strong relationships with their students and deeply care about their well-being. However, they may struggle with setting boundaries and enforcing discipline when necessary.
Educators employ a variety of approaches to create a conducive learning environment. One such approach that has gained attention is indulgent classroom management. Unlike authoritarian or permissive management styles, which may emphasize strict control or leniency, indulgent management takes a more relaxed and accommodating approach. This style prioritizes building positive relationships with students and fostering a supportive and nurturing atmosphere in the classroom. While some critics may argue that indulgent management can lead to lax discipline and lack of accountability, proponents believe that it promotes student well-being, autonomy, and intrinsic motivation.
Features:
To comprehensively understand indulgent classroom management, it’s important to examine its key features and guiding principles. While implementation may vary, the following features are commonly associated with indulgent management:
- Emphasis on Positive Relationships:
- Indulgent management places a strong emphasis on building positive relationships between teachers and students.
- Teachers strive to create a supportive and nurturing classroom atmosphere where students feel valued, respected, and understood.
- By fostering positive relationships, teachers create an environment where students feel comfortable expressing themselves, taking risks, and engaging in learning activities.
- Supportive and Flexible Approach:
- Indulgent teachers adopt a supportive and flexible approach to classroom management, prioritizing empathy and understanding.
- Teachers recognize that each student is unique and may have different needs, interests, and learning styles.
- By being flexible and accommodating, teachers create an environment where students feel supported in their academic and personal growth.
- Minimal Rules and Structure:
- Unlike authoritarian management, which may emphasize strict rules and structure, indulgent management adopts a more relaxed approach.
- Teachers may establish basic guidelines for behavior and academic performance but allow for greater flexibility and discretion in their enforcement.
- The emphasis is on promoting a culture of trust and respect, where students feel empowered to make choices and contribute to the learning environment.
- Focus on Student Well-being:
- Indulgent management prioritizes student well-being and emotional health.
- Teachers recognize the importance of addressing students’ social, emotional, and mental needs in addition to their academic development.
- By creating a supportive and nurturing environment, teachers promote a sense of belonging, acceptance, and emotional safety.
- Encouragement of Self-expression and Creativity:
- Indulgent classrooms encourage students to express themselves creatively and authentically.
- Teachers provide opportunities for students to explore their interests, passions, and talents through creative projects, discussions, and activities.
- By fostering a culture of creativity and self-expression, teachers empower students to develop their unique strengths and identities.
How to Use Indulgent Management in the Classroom?
Implementing indulgent management in the classroom requires a thoughtful and intentional approach that balances support with structure, empathy with accountability. While this approach may not be suitable for every classroom or teaching style, there are certain strategies that educators can employ to effectively utilize indulgent management techniques:
- Build Positive Relationships:
- Invest time and effort in building positive and supportive relationships with students, demonstrating empathy, warmth, and respect in your interactions.
- Get to know your students as individuals, showing genuine interest in their interests, backgrounds, and experiences.
- Create a classroom environment where students feel valued, accepted, and understood, fostering a sense of belonging and connection.
- Provide Emotional Support:
- Recognize and validate students’ emotions, providing a safe space for them to express themselves and seek support when needed.
- Be empathetic and compassionate in your responses to students’ struggles, offering encouragement, reassurance, and guidance.
- Foster a culture of emotional safety and acceptance, where students feel comfortable sharing their thoughts, feelings, and concerns.
- Encourage Self-expression and Creativity:
- Provide opportunities for students to express themselves creatively through art, writing, music, or other forms of expression.
- Encourage students to share their ideas, opinions, and perspectives in class discussions, debates, or presentations.
- Celebrate and value students’ unique talents, interests, and contributions, fostering a culture of creativity and innovation.
- Foster Independence and Responsibility:
- Empower students to take ownership of their learning by providing opportunities for autonomy and self-direction.
- Encourage students to set goals, make decisions, and take initiative in their academic pursuits.
- Provide guidance and support as needed, but allow students the freedom to explore and discover solutions on their own.
- Maintain High Expectations:
- While indulgent management prioritizes support and flexibility, it is important to maintain high expectations for behavior and academic achievement.
- Communicate your belief in students’ abilities and provide the necessary support and resources to help them reach their goals.
- Encourage students to challenge themselves, take risks, and strive for excellence in their academic and personal endeavors.
Discover Your Style
Now that you have learned about the four main classroom management styles, it’s time to reflect on your preferred approach. Consider the following questions:
- Are you more comfortable with high control or low control?
- Do you believe in giving students a voice and encouraging discussions?
- How important are clear rules and consequences?
- Are you willing to invest time and effort in building relationships with your students?
By answering these questions, you can gain insight into your classroom management style and make adjustments as needed.
Take Home
Choosing the right classroom management style is crucial for creating a positive and effective learning environment. Whether you lean towards authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, or indulgent management, understanding your preferred approach will help you develop strategies to engage and motivate your students. Remember, every teacher is unique, and finding the right balance between control and student involvement is key to fostering a successful classroom. Remember, teaching is a lifelong learning process, and there are always opportunities for professional development. If you are interested in further enhancing your classroom management skills, consider exploring the link provided for classroom management professional development training. Keep exploring and refining your teaching style to make a lasting impact on your student’s educational journey.
Happy teaching!
References
- Kami – The Four Common Classroom Management Styles
- LeadSchool – What are the 4 classroom management styles
- Continental Press – Which of the 4 Different Types of Classroom Management
- TeachHUB – Exploring Classroom Management Styles
- ClassPoint – The Classroom Management Styles Guide
- MyGreatLearning – Top 4 classroom management styles
- Exploring Classroom Management Styles – TeachHUB
- Which of the 4 Different Types of Classroom Management – Continental Press
- What are the 4 classroom management styles – LeadSchool
- The Four Common Classroom Management Styles – Kami
- Classroom Behaviour Management: Authoritative Teaching Style – PlanBee







[…] sense of their educational experiences. This understanding enables educators to their instructional approaches to meet the diverse needs and learning styles of students, ensuring that learning is accessible, meaningful, and engaging for […]
[…] classroom settings, one size does not fit all when it comes to instructional techniques. Effective classroom management entails recognizing and embracing the unique learning styles, interests, and preferences of individual students. Utilizing diverse instructional methods like […]
[…] management means establishing a positive and respectful classroom environment where students feel emotionally safe, supported, and empowered to […]
[…] Classroom management refers to your practices and processes to establish an environment where instruction and learning can occur smoothly. It is not making students quiet and passive listeners but goes beyond maintaining discipline; it encompasses creating a supportive, engaging, and organized space that fosters student involvement and cooperation. In this article, we will explore the importance of classroom management and provide strategies for effective implementation. […]
[…] behavior can be a significant challenge in classroom management. Teachers must establish clear misbehavior consequences while addressing the root causes behind […]
[…] Communicative Language Approach encourages many classroom activities that promote active language use and interaction. These activities include pair or group […]
[…] Style Variations: Lecture-style teaching may not cater to students’ diverse learning styles and preferences. Some learners may need help to absorb information through auditory means alone, while others may […]
[…] learning is especially effective for those who struggle with typical classroom learning approaches such as lectures and texts. It offers a different method that enables students to actively engage […]
[…] A learner-centred strategy is another crucial aspect of Pragmatism in education. The needs and interests of the students are highly valued in pragmatic educational theory. Instead of acting as authorities, teachers should act as mentors and facilitators who support their students’ growth as independent and critical thinkers. To provide instruction focused on each student’s needs, educators must be adaptable and willing to change their approaches to the classroom. […]
[…] and retrieval. Moreover, mnemonic techniques can be personalized to suit individual learning styles and preferences, allowing learners to tailor their mnemonic strategies to maximize […]
[…] routines, managing student behavior, and promoting student engagement. Research shows effective classroom management correlates with student achievement and positive social-emotional […]
[…] industrial revolution influenced the earliest approaches to classroom management in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Classrooms, like factories, were designed to produce […]
[…] same task to every student, educators can provide various options catering to different learning styles and preferences. For instance, in a literature class, students could write an essay, create a visual […]
[…] that educators can implement to enhance the learning experiences of students. We will discuss approaches such as flipped classrooms, project-based learning, gamification, personalized learning, collaborative learning spaces, […]